阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer disease, AD),又称老年痴呆症,是最常见的一种痴呆形式,主要病因是大脑组织受损、缺乏某些重要化学物质而引起智力下降。由于AD病因不明,尚无特效药物治疗,故已成为人们关注的重大社会问题,是继心、脑血管疾病和癌症后危害老年健康的“第三大杀手”。随着人们平均寿命增长、人口老龄化的加剧,AD患者急速增加,中国现已有近1000万人患此病。阿尔茨海默病(AD)已经对人类健康造成严峻挑战,给社会和家庭带来了沉重负担,给医疗体系及患者家庭带来巨大压力。阿尔茨海默病的早期诊断和治疗是当前最热门的研究方向之一,小编这次给大家整理近年来AD研究的分子机制和主要信号通路。
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种使人衰弱的神经退行性疾病,它的特征是由脑细胞之间的斑块沉积物组成。这些斑块由称为淀粉样蛋白的分子组成,该分子导致形成于脑细胞内的由tau制成的缠结扭曲纤维。这些会引起脑细胞死亡,据此认为是导致阿尔茨海默症患者记忆力减退和痴呆症状的原因。Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a debilitating neurodegenerative disorder. It is characterised by plaques made up of deposits between brain cells. These plaques are composed of a molecule called amyloid which leads to the formation of tangled twisted fibres made from tau, which is found within brain cells. This causes the death of brain cells, which is thought to bring about the symptoms of memory loss and dementia.
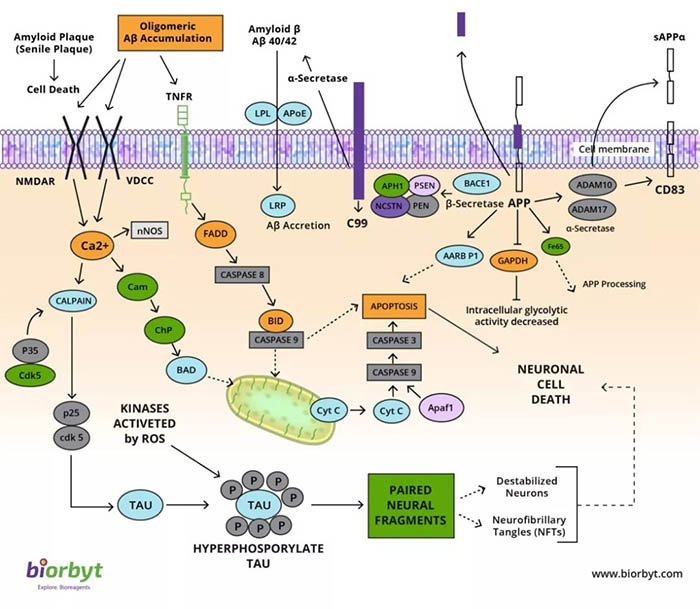
跨膜蛋白APP(淀粉样前体蛋白)裂解后形成的Aβ沉积是目前被认为是AD发病的重要原因。APP最初被α-分泌酶切割以产生sAPP和C83羧基末端片段。APP最初被α-分泌酶切割以产生sAPP和C83羧基末端片段。 sAPP的存在与正常的突触信号相关,并导致突触可塑性,学习和记忆,情绪行为和神经元存活。在疾病状态下,APP被β-分泌酶和γ-分泌酶顺序切割,释放出称为A40-42的细胞外片段。该片段的聚集导致A40-42寡聚化和噬菌斑形成,从而引起神经毒性,导致离子通道受阻,钙稳态下降,线粒体氧化应激,能量代谢受损,葡萄糖调节异常,最终导致神经元细胞死亡。 CDK5和其他激酶(例如GSK3,PKC,PKA和Erk2)也被细胞中产生的活性氧激活。这导致Tau的过度磷酸化,导致Tau与微管解离,从而导致细胞内Tau蛋白的微管去稳定化和寡聚化。神经纤维缠结由于Tau寡聚而形成,并导致神经元凋亡。
The processing of the integral membrane protein APP (Amyloid Precursor Protein) is fundamental to the progression of this disease. APP is initially cleaved by α-secretase to generate sAPP and a C83 carboxy-terminal fragment. The presence of sAPP is associated with normal synaptic signalling and results in synaptic plasticity, learning and memory, emotional behaviours, and neuronal survival. In the disease state, APP is cleaved sequentially by β-secretase and γ-secretase to release an extracellular fragment called A40-42. Aggregation of this fragment results in A40-42 oligomerization and plaque formation causing neurotoxicity, resulting in blocked ion channels, disruption of calcium homeostasis, mitochondrial oxidative stress, impaired energy metabolism, abnormal glucose regulation, and ultimately neuronal cell death. CDK5 and other kinases such as GSK3, PKC, PKA, and Erk2 are also activated by reactive oxygen species generated in the cell. This leads to hyperphosphorylation of Tau resulting in the dissociation of Tau from the microtubule, leading to microtubule destabilization and oligomerization of the Tau protein within the cell. Neurofibrillary tangles form because of Tau oligomerization and lead to apoptosis of the neuron.
1. Gratuze M, et al. Mutual Relationship between Tau and Central Insulin Signalling: Consequences for AD and Tauopathies? Neuroendocrinology. 2018;107(2):181-195. doi: 10.1159/000487641. Epub 2018 Feb 13.
2. Pereira CD, et al. ABC Transporters Are Key Players in Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;61(2):463485. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170639.
3. Pedros I, et al. Molecular links between early energy metabolism alterations and Alzheimer's disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016 Jan 1;21:8-19. Review.